词嵌入的目标 获取词在向量空间中的表示,用向量去表示词义→ 获取一个关于词典的矩阵
0. 写在前面
基础知识需要:词嵌入的简单理解(可以我看之前的文章或者视频),统计学的一点点基础概念,神经网络的一丢丢了解
内容预览:
-
skip-gram 的核心思想
-
skip-gram从直觉上的通俗解释
-
skip-gram 损失函数的数学推导
1. 从直觉(intuition)上通俗理解skip-gram
最合乎直觉(intuition)的假设-分布假设:相似的词往往出现在同一语境中(例如,在眼睛或检查等词附近)。
==语义相似的词往往会相邻出现,不相似的词不会相邻出现==
案例:

==颜色标记相同的词(相邻的)语义上是相似的==
目标: 获取词向量的最佳表示,就是获取一个 $\theta \in R^{V×N}$ ,如下,V代表词典大小,N代表每个词对应词向量的维度
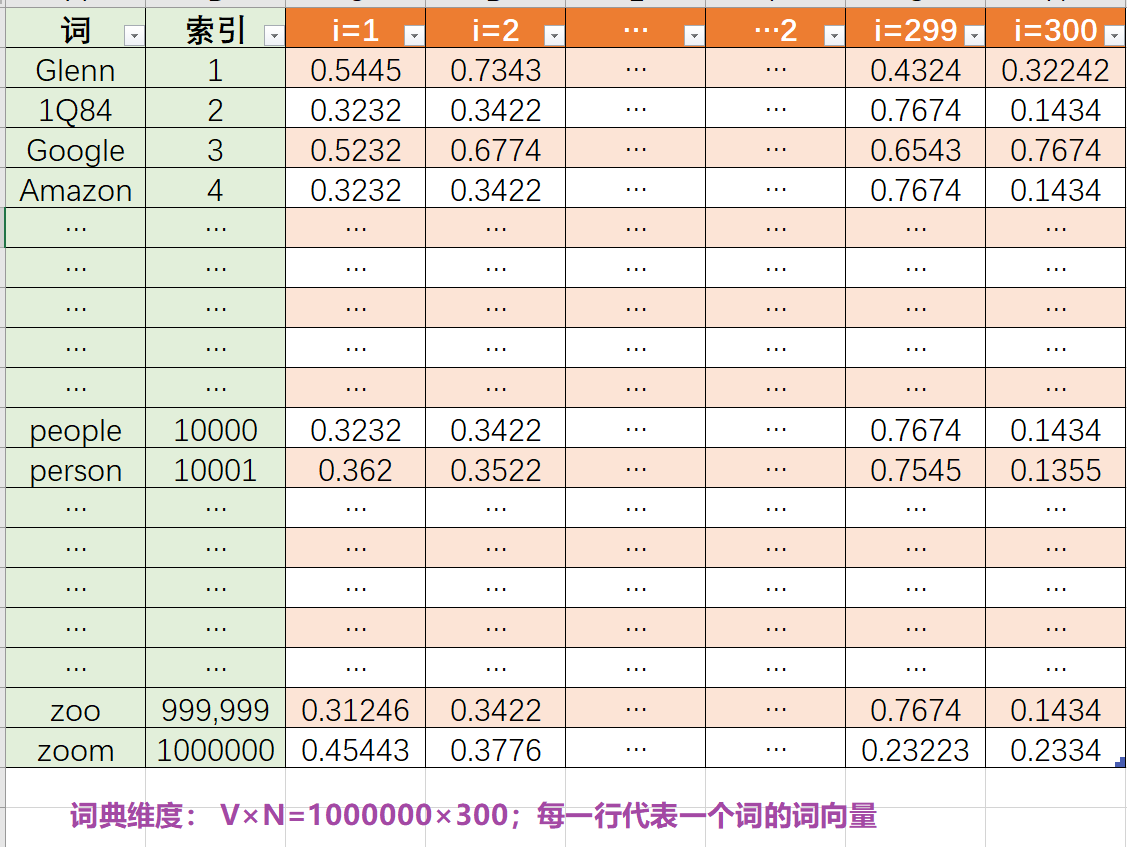
**question 1: 如何 数学化 分布假设(简化:相邻的词语义相似) 实现词向量获取的目标?**
maybe 预测(说一句话的时候是一个词一个词蹦出来的,是不是 已知某个词 预测下一个词呢?或者已知某个词 预测周围的语境词呢?)
给定一句话: the man who passes the sentence should swing the sword
pS: ${w_{cj}}$代表第j个相邻词context word,${w_{nci}}$代表第i个非相邻词 not context word
| 1 | 2 | 3 | 4 | 5 | 6 | 7 | 8 | 9 | 10 |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| the | man | who | passes | the | ==sentence== | should | swing | the | sword |
| $w_{nc1}$ | $w_{nc2}$ | $w_{nc3}$ | $\pmb }$ | $\pmb }$ | ==$\pmb {w_{center}}$== | $\pmb {w_{c3}}$ | $\pmb {w_{c4}}$ | $ w_{nc4}$ | $w_{nc5}$ |
目标数学化:通过最大化 给定中心词下相邻词的概率,间接获取词向量表示
\[\underset{\theta}{\operatorname{argmax}}p(w_{c1},w_{c2},w_{c3},w_{c4}|w_{center},\theta)\]2. 将目标表示成一个神经网络优化任务进行实现:损失函数的推导
\[\underset{\theta}{\operatorname{argmax}}p(w_{c1},w_{c2},...,w_{cC}|w_{center},\theta) \\ C-context\ word 的总数,如(1)中w_{c4}的4\]step1 简单化任务:假设语境词context word只有一个,实际当中有多个
\[w_{c1},w_{c2},...,w_{cC}→w_{context}\] \[\underset{\theta}{\operatorname{argmax}}p(w_{c1},w_{c2},...,w_{cC}|w_{center},\theta) →\underset{\theta}{\operatorname{argmax}}p(w_{context}|w_{center},\theta)\]任务定义:
task: 基于中心词$w_{center}$预测周围词$w_{context}$
input: 中心词 center word $w_{center}$
output:语境词or相邻词 context words $w_{context}$
optimizing:
\[\underset{\theta}{\operatorname{argmax}}p(w_{context}|w_{center};\theta)\] \[\underset{\theta}{\operatorname{argmax}} p(w_{context}|w_{center};\theta)=\frac{p(w_{context}w_{center})}{p(w_{center})}\]**question 2 : 如何计算$\frac{p(w_{context}w_{center})}{p(w_{center})}$?**
根据概率公式:
\[P(A_{j}|B)=\dfrac{P(A_jB)}{P(B)}=\dfrac{P(A_j B)}{\sum\limits_{i=1}^n{P(A_i B)}}\]推导出:
\[\frac{(w_{context}w_{center})} {p(w_{center})}=\frac{p(w_{context}w_{center})} {\sum^V_{i=1}p(w_iw_{center})} \\ V-词典大小,即词典中词的个数 \\ 词典=w_1,w_2,...,w_{context},...,w_V\]**question 3: 如何计算$p(w_{i}w_{j})$?**
==$w_i,w_j$共同出现的可能性$\Leftrightarrow w_i,w_j$相似程度$\Leftrightarrow w_i,w_j$内积大小,内积越大越相似==
由(9)→(10)
\[p(w_{i}w_{j})\Leftrightarrow similarity(w_i,w_j)\Leftrightarrow w_i^T\cdot w_j\Leftrightarrow exp(w_i^T\cdot w_j) \\w_i,w_j\in R^n\] \[\underset{\theta}{\operatorname{argmax}} p(w_{context}|w_{center};\theta)=\frac{p(w_{context}w_{center})}{p(w_{center})} =\frac{p(w_{context}w_{center})}{\sum^V_{i=1}p(w_iw_{center})}=\frac{exp(w_{context}^T\cdot w_{center})}{\sum^V_{i=1}exp(w_i^T \cdot w_{center})}\]step2 规范化任务:还原多个context word的目标
由(10)(12)→(13) \(w_{context}→w_{c1},w_{c2},...,w_{cj},...,w_{cC}\)
\[p(x_1,x_2, ..., x_C)=p(x_1)×p(x_2)×,...,×p(x_C)\] \[\underset{\theta}{\operatorname{argmax}}p(w_{c1},w_{c2},...,w_{cC}|w_{center},\theta)=\prod\limits_{j=1}^C\frac{exp(w_{cj}^T\cdot w_{center})}{\sum^V_{i=1}exp(w_i^T \cdot w_{center})}\]step3 将目标转化为 最小化代价函数cost function $J(\theta)$
对于(13)进行:
- 最大化→最小化 加负号
- 方便计算: 取对数$log$
得到(14)→(15)
\[\underset{\theta}{\operatorname{argmax}}p(w_{c1},w_{c2},...,w_{cC}|w_{center},\theta)\Leftrightarrow \underset{\theta}{\operatorname{argmin}}p(w_{c1},w_{c2},...,w_{cC}|w_{center},\theta)=-log\prod\limits_{j=1}^C\frac{exp(w_{cj}^T\cdot w_{center})}{\sum^V_{i=1}exp(w_i^T \cdot w_{center})}\] \[J(\theta)= -log\prod\limits_{j=1}^C\frac{exp(w_{cj}^T\cdot w_{center})}{\sum^V_{i=1}exp(w_i^T \cdot w_{center})} = - \sum\limits_{j=1}^{C} log \frac{exp(w_{cj}^T\cdot w_{center})}{\sum^V_{i=1}exp(w_i^T \cdot w_{center})} \\ = -log \sum\limits_{j=1}^{C}exp(w_{cj}^T\cdot w_{center}) + C\cdot {\sum^V_{i=1}exp(w_i^T \cdot w_{center})}\]计算成本是非常高的,因为每一个中心词都要计算 $C\cdot {\sum^V_{i=1}exp(w_i^T \cdot w_{center})}$,
通过负采样: softmax(从所有词中找出周围词)→sigmoid(分类是否是周围词)
负采样的词如何选择:对词频做归一化,然后做平滑 ,使得出现词频少的部分也能较多的采样
补充说明:
1. 向量的相似性计算
如果一个词的嵌入向量与目标嵌入相似,它就有可能出现在目标附近。为了计算这些密集嵌入之间的相似性,我们依靠这样的直觉:两个向量如果有很高的点积就会相似(毕竟余弦只是一个归一化的点积):
\(similarity(w,c)\approx w^T\cdot c\\ w,c\in R^n\) 参考文献
-
[Demystifying Neural Network in Skip-Gram Language Modeling Pythonic Excursions (aegis4048.github.io)](https://aegis4048.github.io/demystifying_neural_network_in_skip_gram_language_modeling) -
[Understanding Multi-Dimensionality in Vector Space Modeling Pythonic Excursions (aegis4048.github.io)](https://aegis4048.github.io/understanding_multi-dimensionality_in_vector_space_modeling)